Drones are getting more and more popular for commercial use. Drones are also becoming more familiar to consumers as they’re now widely available for purchase and can be operated by anyone with access to the internet. As a result, retailers, delivery services and other businesses are becoming interested in using drones for their own supply chain initiatives. Drones have many uses and there are no laws restricting the use of drones by businesses operating within an industrial park, remote location or other secure site where operations do not pose a risk to public safety and privacy. In fact, one of the biggest challenges that local businesses across the globe face when it comes to using drones is legislation on legislation. Legislation varies from country to country as well as state to state on how they govern drone use. If you plan on using drones in your local area or state (U.S.) check with local law enforcement agencies before you begin operating drones in your area.
What types of drones are there?
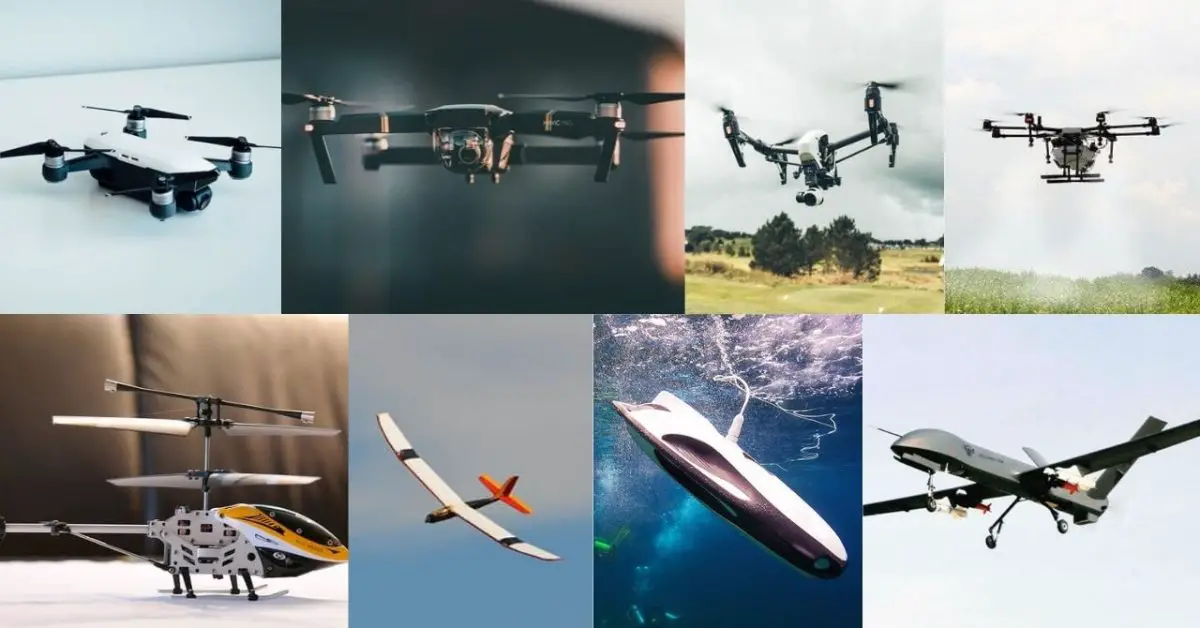

There are three main types of drones when it comes to commercial use: fixed-wing, rotary and multi-rotor. Fixed-wing drones have a fixed wing and a center body with a motor used to propel the drone. Multi-rotor drones have many rotors that can be controlled by a single pilot. Fixed-wing drones include fixed-wing drones such as fixed-wing drones that operate like a plane, hover or glider and unmanned helicopters. Fixed-wing drones that operate like a plane are used for mapping, surveying, photography and videography. Aircraft are the most common type of drone used for commercial use. They are autonomous and follow a pre-set route. The size of the aircraft used for commercial use will depend on the distance that needs to be flown. Small drones for commercial use are usually about the size of a small bird, while large aircraft can fly at altitudes of up to 10,000 feet.
Laws on using drones for deliveries

Since drone technology is still relatively new, not many laws have been put in place to govern their usage. The majority of the laws that govern drone usage are based off of similar laws that regulate the usage of manned aircraft. In general, drone usage is governed by the same laws that govern the usage of manned aircraft. There are three main types of laws that govern drone usage: Aviation Law, Liability Law and Security Law. Aviation Law is a set of laws that govern all types of aircraft including manned, unmanned and remote-controlled aircraft. Under Aviation Law, drone operators are required to register their aircraft, keep their aircraft within visual line of sight (VLOS) of the operator at all times and stay at least 500 feet away from all prohibited and restricted areas.
How to use a drone for deliveries
Drones can be used for commercial purposes for various activities, including commercial photography, real estate inspection and inspections of infrastructure, like power grids and water systems. Delivery companies can also utilize drones for their operations. In order to use a drone for deliveries, the drone operator will have to obtain a remote pilot certificate from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). After the operator has received the pilot certificate, the operator will be able to fly their drone for commercial use in accordance with the rules and regulations set by the FAA. The operator will also be required to register their drone with the FAA. To ensure safety, delivery companies are required to follow certain rules and regulations while using drones. The rules and regulations include: – Operate drones during daylight or limited visibility conditions. – Never fly a drone in a congested area or a densely populated area. – Never fly a drone over the property of another person.
Requirement when it comes to using drones for deliveries

There are three basic requirements that need to be met before a drone can be used for commercial use. First and foremost is that the drone operator must be able to pass a written test and a practical test. The written test tests the operator’s knowledge on regulations and rules and the practical test tests the operator’s ability to control the drone. Secondly, the operator must be able to obtain a remote pilot certificate and a Remote-Airspace Operator Certificate from the FAA. The FAA will only issue these certificates to companies that have been operating for at least two years and have completed all applicable FAA requirements. Thirdly, the operator must be able to comply with local and state laws.
What’s the difference between “Commercial Use” and “Drones For Commercial Use?”

A business can use a drone for non-commercial uses, but commercial drone use generally involves making money by selling products or services. Commercial use typically refers to the use of a drone for delivering commercial goods, such as food or beverages, or for performing aerial photography or videography. The FAA defines commercial use as things like making maps, surveying land, flying a support function for real estate appraisal or inspection, finding a person who’s lost, flying a supply chain for a business, or testing new products in a controlled environment. For example, a nearby restaurant could order a pizza using a drone to ensure the quality of the product. Other businesses could use a drone to inspect their power grid to make sure there is no damage. Real estate companies could use a drone to inspect a building to make sure there are no structural issues.
Why you should have a code of practice for drone usage?
A code of practice is a set of rules shared by drone operators that helps promote safety when using drones. A code of practice typically includes ground rules, operational guidelines and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
As the drone market continues to grow, more and more businesses are beginning to explore the benefits of using drones for their operations. However, because of the lack of regulation when it comes to drones, it can be difficult for businesses to navigate the regulatory landscape and use drones safely. Drones offer significant benefits to businesses, but they also pose an increased risk if used without proper training and knowledge. By following these guidelines, you can use drones safely and effectively.